Publications
2022

Chilev, Chavdar; Simeonov, Evgeni; Dimitrova, Borislava; Yonkova, Velislava; Pietsch, Swantje; Heinrich, Stefan; Peshev, Dimitar
Valorization of waste lavender residue from the essential oil industry for production of rosmarinic acid – a study on the solid-liquid extraction Journal Article Forthcoming
In: Journal of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, Forthcoming.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Journal Article
@article{nokey,
title = {Valorization of waste lavender residue from the essential oil industry for production of rosmarinic acid – a study on the solid-liquid extraction},
author = {Chavdar Chilev and Evgeni Simeonov and Borislava Dimitrova and Velislava Yonkova and Swantje Pietsch and Stefan Heinrich and Dimitar Peshev},
editor = {Bogdana Koumanova},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/02_Manuscript.pdf},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-00-00},
journal = {Journal of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy},
abstract = {The possibility for valorization of the waste lavender residue from the essential oil industry via solvent extraction was studied. The plant residue of Lavandula angustifolia, from which the lavender oil is extracted through steam distillation, contains Key Biologically Active Components (KBAC) such as: rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, luteolin. The feasibility of the solvent extraction for their isolation was assessed by comparison of the kinetics and equilibrium of extraction of KBAC from spent and raw plant material (collected from the same batch before the steam distillation) using different solvent compositions. The parameters of the extraction process were experimentally and numerically optimized. To determine the most efficient solvent, two pure and two mixed solvents were tested: pure water, 99.9% Ethanol and their mixtures – (40% and 60% Ethanol). Using 40% ethanol as extraction solvent resulted in maximum recovery of KBAC. A mathematical model for the solid-liquid extraction from lavender materials was developed. The values of the model parameters were determined using the Regular regime method. A four-parameter empirical model for prediction of the effective diffusivity, D_eff, was also applied. The model adequacy was experimentally verified. Based on the theoretical and experimental results KBAC recovery the following extraction conditions were recommended: extraction time - 30min, temperature - 30℃, liquid-solid ratio - 0.01 m^3⁄kg, and 40% Ethanol as an extraction solvent
Keywords: solid-liquid extraction, kinetics, lavender, modeling, rosmarinic acid, essential oil.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).},
keywords = {Journal Article},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Keywords: solid-liquid extraction, kinetics, lavender, modeling, rosmarinic acid, essential oil.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).
2021

Peshev, Dimitar; Dimitrova, Borislava; Penchev, Petko; Chilev, Chavdar
Abstract book Euromembrane, Euromembrane 2021 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {New possibilities for the valorisation of waste aqueous fractions from the essential oil industry using nanofiltration.},
author = {Dimitar Peshev and Borislava Dimitrova and Petko Penchev and Chavdar Chilev},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Poster_Peshev-1.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-12-02},
booktitle = {Abstract book Euromembrane},
organization = { Euromembrane 2021},
abstract = {The possibility to fractionate hydrosols and extracts (residual waters) from the steam and hydrodistillation of essential
oil plants using nanofiltration was investigated. The separation performance of five commercial nanofiltration
membranes with respect to key biologically active components of the studied waste aqueous fractions was predicted
based on regression models [1,2]. Membranes of different MWCO, structure and composition were analysed.
Descriptors in the models for the membrane rejection were the membrane MWCO and zeta potential as well as
solute’s molecular weight, octanol-water partition coefficient (log P) and charge at pH of the solution (or pKa). For
consistency of the results, log P and pKa of all studied components were calculated according to the COSMO-RS
method, which has the quantum-chemical basis of the Conductor-like Screening Model (COSMO). The calculations
were performed using the BIOVIA COSMOsuite software package package (Dassault Systèmes SE). The theoretical
assessment was subjected to experimental verification by nanofiltration of hydrosols and extracts collected from
industrial facilities using commercial polyethersulfone and composite polyamide membranes. The results showed that
independently of the membrane material, the polymeric membranes exhibit high retention capability against charged
solutes such as the contained in the residual waters phenolic acids. Since the pKa of the phenolic compounds,
representatives of the flavonoid family is within the range of pH of the aqueous extracts, their retention or permeation
could be controlled by slight variations of the pH. The dissolved in the aqueous fractions essential oil components
would be easily permeating through the membranes. These results clearly demonstrated the viability of nanofiltration
for isolation of refined polyphenolic fractions from the extracts effluents and for recovery of phenethyl alcohol and
eugenol from hydrosols of Rosa damascena and cloves respectively.
Reference 1:
K. Boussu, C. Vandecasteele, B. Van der Bruggen, J. Mem. Sci., 310, 51 (2008)
Reference 2:
D. Peshev, Bul. Chem. Commun., 52, 4, 532 (2020)
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
oil plants using nanofiltration was investigated. The separation performance of five commercial nanofiltration
membranes with respect to key biologically active components of the studied waste aqueous fractions was predicted
based on regression models [1,2]. Membranes of different MWCO, structure and composition were analysed.
Descriptors in the models for the membrane rejection were the membrane MWCO and zeta potential as well as
solute’s molecular weight, octanol-water partition coefficient (log P) and charge at pH of the solution (or pKa). For
consistency of the results, log P and pKa of all studied components were calculated according to the COSMO-RS
method, which has the quantum-chemical basis of the Conductor-like Screening Model (COSMO). The calculations
were performed using the BIOVIA COSMOsuite software package package (Dassault Systèmes SE). The theoretical
assessment was subjected to experimental verification by nanofiltration of hydrosols and extracts collected from
industrial facilities using commercial polyethersulfone and composite polyamide membranes. The results showed that
independently of the membrane material, the polymeric membranes exhibit high retention capability against charged
solutes such as the contained in the residual waters phenolic acids. Since the pKa of the phenolic compounds,
representatives of the flavonoid family is within the range of pH of the aqueous extracts, their retention or permeation
could be controlled by slight variations of the pH. The dissolved in the aqueous fractions essential oil components
would be easily permeating through the membranes. These results clearly demonstrated the viability of nanofiltration
for isolation of refined polyphenolic fractions from the extracts effluents and for recovery of phenethyl alcohol and
eugenol from hydrosols of Rosa damascena and cloves respectively.
Reference 1:
K. Boussu, C. Vandecasteele, B. Van der Bruggen, J. Mem. Sci., 310, 51 (2008)
Reference 2:
D. Peshev, Bul. Chem. Commun., 52, 4, 532 (2020)
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)
Chilev, Chavdar; Peshev, Dimitar
Abstract book Euromembrane, Euromembrane 2021 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {Utilization of the waste lavender residue from the essential oil industry via extraction and membrane filtration},
author = {Chavdar Chilev and Dimitar Peshev},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Poster_Chilev.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-12-02},
urldate = {2021-12-02},
booktitle = {Abstract book Euromembrane},
organization = {Euromembrane 2021},
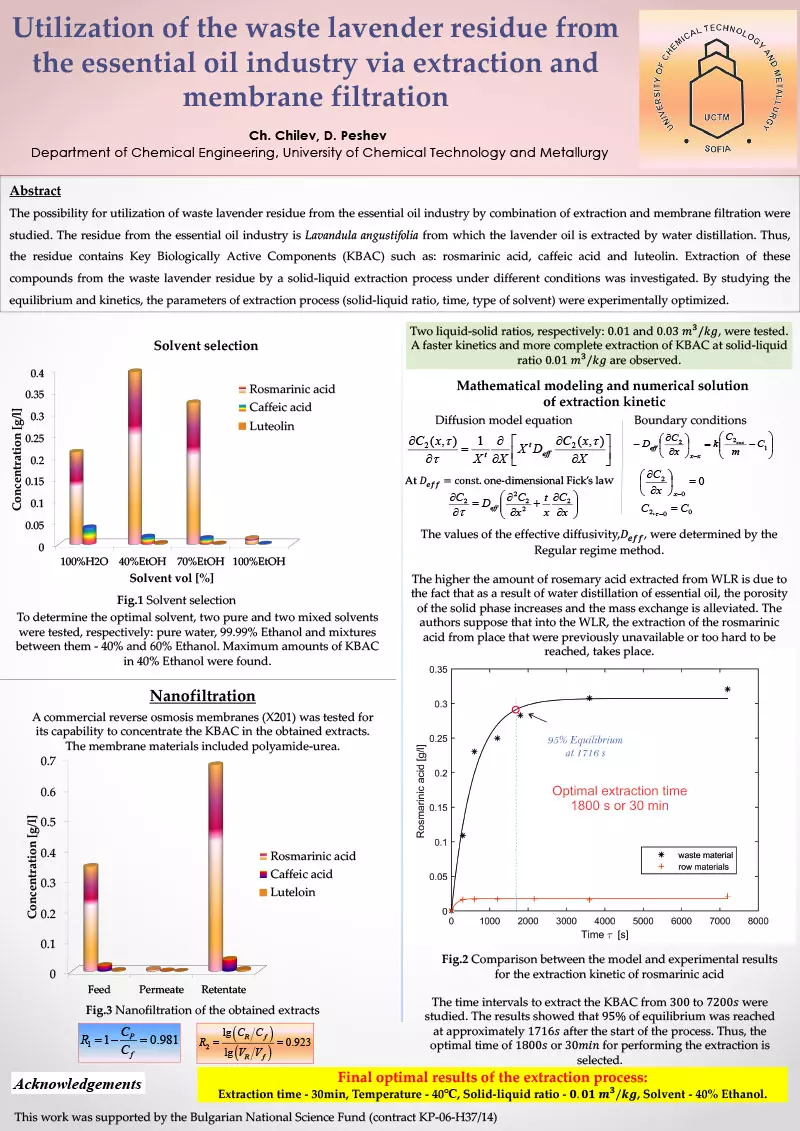
abstract = {The possibility for utilization of WLR from the essential oil industry by combination of extraction and membrane
filtration were studied. The WLR from the essential oil industry is Lavandula angustifolia from which the lavender oil is
extracted by steam distillation. Thus, the residue contains KBAC -rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, quercetin and luteolin.
Extraction of KBAC from WLR by extraction under different conditions was investigated. By studying the equilibrium
and kinetics, the parameters of the extraction process (solid-liquid ratio, time, type of solvent) were experimentally
optimized. The time intervals to extract the KBAC from 600 to 10800s were studied. The results showed that
equilibrium was reached at approximately 7000s after the start of the experiment. Thus, a time of 7200s for performing
the extraction is selected. Two liquid-solid ratios, respectively: 0.01 and 0.03 , were tested. A faster kinetics and more
complete extraction of KBAC at solid-liquid ratio 0.01 are observed. To determine the optimal solvent, four solvents
were tested, respectively: pure water, 99.99% Ethanol and mixtures between them - 40% and 60% Ethanol. Maximum
amounts of KBAC in 40% Ethanol were found. Thus, the optimal conditions under which the experiments were
performed were determined: temperature - 40℃, solid-liquid ratio - and the solvent - 40% Ethanol.
The extracts are aqueous-alcoholic solutions containing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds. A range of
commercial NF (DL, SUEZ (GE); NP030, NADIR, Puramem 200, Evonik MET) and RO (X201, TriSep) membranes were
tested for their capability to fractionate or concentrate the KBAC in the obtained extracts. The use of membranes with
different structure and composition of the selective layer, and with different hydrophobicity respectively, allowed for
qualitative conclusions on the effects from the KBAC components interactions with the membranes. The adverse depot
effect due to the adsorption of solutes in the membranes during batch filtration was evaluated. The membrane
materials included modified polyimide (Duramem 200), polyethersulfone (NP030), polyamide (DL) and polyamide-urea
(X201).
Keywords: essential oil, nanofiltration, membrane, fractionation, extraction.
Abbreviations:
WLR - Waste Lavender Residue
KBAC - Key Biologically Active Components
RO - Reverse Osmosis
NF - Nanofiltration
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
filtration were studied. The WLR from the essential oil industry is Lavandula angustifolia from which the lavender oil is
extracted by steam distillation. Thus, the residue contains KBAC -rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, quercetin and luteolin.
Extraction of KBAC from WLR by extraction under different conditions was investigated. By studying the equilibrium
and kinetics, the parameters of the extraction process (solid-liquid ratio, time, type of solvent) were experimentally
optimized. The time intervals to extract the KBAC from 600 to 10800s were studied. The results showed that
equilibrium was reached at approximately 7000s after the start of the experiment. Thus, a time of 7200s for performing
the extraction is selected. Two liquid-solid ratios, respectively: 0.01 and 0.03 , were tested. A faster kinetics and more
complete extraction of KBAC at solid-liquid ratio 0.01 are observed. To determine the optimal solvent, four solvents
were tested, respectively: pure water, 99.99% Ethanol and mixtures between them - 40% and 60% Ethanol. Maximum
amounts of KBAC in 40% Ethanol were found. Thus, the optimal conditions under which the experiments were
performed were determined: temperature - 40℃, solid-liquid ratio - and the solvent - 40% Ethanol.
The extracts are aqueous-alcoholic solutions containing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds. A range of
commercial NF (DL, SUEZ (GE); NP030, NADIR, Puramem 200, Evonik MET) and RO (X201, TriSep) membranes were
tested for their capability to fractionate or concentrate the KBAC in the obtained extracts. The use of membranes with
different structure and composition of the selective layer, and with different hydrophobicity respectively, allowed for
qualitative conclusions on the effects from the KBAC components interactions with the membranes. The adverse depot
effect due to the adsorption of solutes in the membranes during batch filtration was evaluated. The membrane
materials included modified polyimide (Duramem 200), polyethersulfone (NP030), polyamide (DL) and polyamide-urea
(X201).
Keywords: essential oil, nanofiltration, membrane, fractionation, extraction.
Abbreviations:
WLR - Waste Lavender Residue
KBAC - Key Biologically Active Components
RO - Reverse Osmosis
NF - Nanofiltration
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)

Chilev, Ch.; D.Peshev,; Lazarova, N.
Extraction of essential oil from cloves using steam and hydro distillation Conference
Book of abstracts of the 67th Scientific Conference with International Participation "Food Science, Engineering and Technology - 2020", UFT, Plovdiv, Bulgaria University of Food Technology - Plovdiv , 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {Extraction of essential oil from cloves using steam and hydro distillation},
author = {Ch. Chilev and D.Peshev and N. Lazarova},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Poster_1-1.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-10-23},
urldate = {2021-10-23},
booktitle = {Book of abstracts of the 67th Scientific Conference with International Participation "Food Science, Engineering and Technology - 2020"},
publisher = {University of Food Technology - Plovdiv },
organization = {UFT, Plovdiv, Bulgaria},
abstract = {Essential oils are used in a wide variety of consumer goods such as detergents, toilet products, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, confectionery food products, soft drinks, distilled alcoholic beverages and insecticides. The extracts of cloves have a pleasant smell, and direct practical applications as a flavoring agent, antioxidant, antifungal agent, local anesthetic, and nutraceutical. The goal of this study is to isolate the natural product, essential oil, from cloves using the steam and water distillation. Both techniques are often used in industry to essential oils manufacturing. The experiments and detailed procedures of water and steam distillation are developed and presented. The optimal clove-to-distillate ratio [g(cloves)/ml(obtained distillate)] with respect to total oil production were determined. The ratio was varied between 0.125 g/mL and 0.0625g/mL. It was found that the optimal ratio of clove-to-distillate was 0.0833 g/mL. The antibacterial activity of the essential oils obtained by two present techniques was determined by the disk diffusion method against Escherichia coli K12 and Bacillus subtilis 3562. The antioxidant activity of the samples was also analysed by the DPPH free radical method where a gallic acid was used as a reference solution.
This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)

Lazarova-Zdravkova, Nevena; Tsanova, D.; Stoyanova, Y.; Chilev, Ch.; Georgieva, N.; Peshev, Dimitar
Study of the biological activity of essential oil-water mixtures Conference
Book of abstracts of the 67th Scientific Conference with International Participation "Food Science, Engineering and Technology - 2020", University of Food Technology - Plovdiv UFT, Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {Study of the biological activity of essential oil-water mixtures},
author = {Nevena Lazarova-Zdravkova and D. Tsanova and Y. Stoyanova and Ch. Chilev and N. Georgieva and Dimitar Peshev},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Poster_2-1.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-10-23},
booktitle = {Book of abstracts of the 67th Scientific Conference with International Participation "Food Science, Engineering and Technology - 2020"},
publisher = {UFT, Plovdiv, Bulgaria},
organization = {University of Food Technology - Plovdiv},
abstract = {This study aimed to investigate the biological activity of aqueous mixtures of two essential oils. The mixtures were prepared by mixing certain amounts of lavender and clove oils with distilled water at room temperature. In the case of lavender oil, a relatively clear saturated aqueous phase was obtained after mixing with excess of the essential oil. The clove oil formed stable oil-in-water emulsions. The antibacterial activity of lavender oil and its aqueous solution were tested against two model bacterial strains. The growth of Escherichia coli K12 and Bacillus subtilis 3562 in the presence of the analysed samples was determined in 96-well microplates and also by a disk diffusion test (Kirby–Bauer test). The results showed that the lavender aqueous solution did not exhibit antibacterial activity against both – the Gram-negative and Gram-positive strains but the oil itself indicated inhibition zones of around 11.7 mm during the tests against B. subtilis 3562. The DPPH free radical method showed no antioxidant activity for the lavender aqueous solution of lavender oil. At the same time the pure lavender oil exhibit low activity compared to the gallic acid (used as a reference) and the clove essential oil. The inhibitory effect of the lavender samples were further compared with the essential oil from clove and its oil-in-water emulsion.
Keywords: antibacterial activity, antioxidant activity, essential oils
Abbreviations:
DPPH – 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)wledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
Keywords: antibacterial activity, antioxidant activity, essential oils
Abbreviations:
DPPH – 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)wledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)
Peshev, Dimitar; Lazarova-Zdravkova, Nevena; Chilev, Chavdar
Book of abstracts of the 67th Scientific Conference with International Participation "Food Science, Engineering and Technology - 2020", University of Food Technology - Plovdiv UFT, Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags:
@conference{nokey,
title = {Theoretical assessment of the possibility for fractionation of waste aqueous fractions from the essential oil industry using nanofiltration.},
author = {Dimitar Peshev and Nevena Lazarova-Zdravkova and Chavdar Chilev},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Poster_3-1.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-10-23},
booktitle = {Book of abstracts of the 67th Scientific Conference with International Participation "Food Science, Engineering and Technology - 2020"},
publisher = {UFT, Plovdiv, Bulgaria},
organization = {University of Food Technology - Plovdiv},
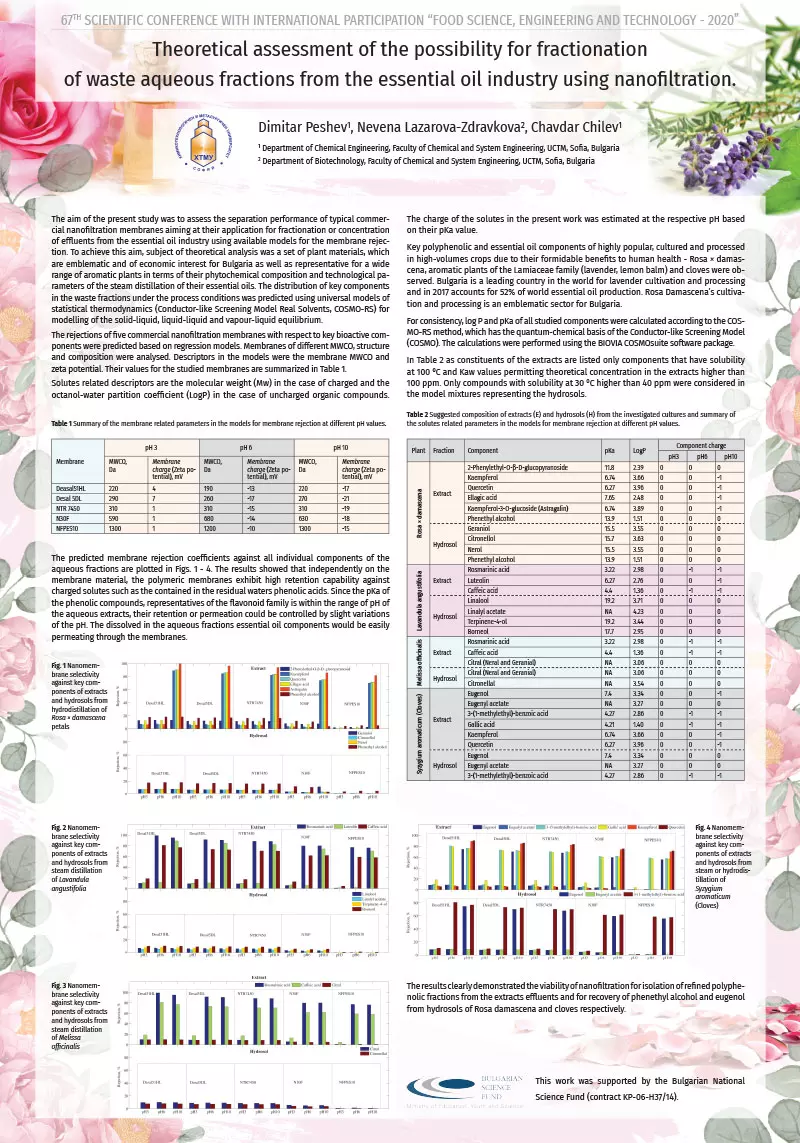
abstract = {The possibility to fractionate hydrosols and extracts (residual waters) from the distillation of essential oil plants using nanofiltration was investigated. The rejections of five commercial nanofiltration membranes with respect to key bioactive components were predicted based on regression models. Membranes of different MWCO, structure and composition were analysed. Descriptors in the models were the membrane MWCO and zeta potential as well as the molecular weight, log P and pKa of the solute. For consistency, log P and pKa of all studied components were calculated according to the COSMO-RS method, which has the quantum-chemical basis of the Conductor-like Screening Model (COSMO). The calculations were performed using the BIOVIA COSMOsuite software package. The results showed that independently on the membrane material, the polymeric membranes exhibit high retention capability against charged solutes such as the contained in the residual waters phenolic acids. Since the pKa of the phenolic compounds, representatives of the flavonoid family is within the range of pH of the aqueous extracts, their retention or permeation could be controlled by slight variations of the pH. The dissolved in the aqueous fractions essential oil components would be easily permeating through the membranes.
Keywords: essential oil, nanofiltration, membrane, fractionation, hydrosol, residual water, phenolic compounds, COSMO-RS
Abbreviations:
MWCO – Molecular Weight Cut-Off
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
Keywords: essential oil, nanofiltration, membrane, fractionation, hydrosol, residual water, phenolic compounds, COSMO-RS
Abbreviations:
MWCO – Molecular Weight Cut-Off
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)

Йорданов, Камен
Извличане на биоактивни компоненти при екстракция от Lavandula angustifolia Bachelor Thesis
2021.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Bachelor Thesis
@bachelorthesis{nokey,
title = {Извличане на биоактивни компоненти при екстракция от Lavandula angustifolia},
author = {Камен Йорданов},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Diplom_work_Iordanov.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-10-15},
urldate = {2021-10-15},
keywords = {Bachelor Thesis},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {bachelorthesis}
}

Сараджова, Християна
Оползотворяване на лавандуловия остатък от производството на етерично масло чрез екстракция Bachelor Thesis
2021.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Bachelor Thesis
@bachelorthesis{nokey,
title = {Оползотворяване на лавандуловия остатък от производството на етерично масло чрез екстракция},
author = {Християна Сараджова},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Diplom_work_Saradzhova.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-10-15},
urldate = {2021-10-15},
keywords = {Bachelor Thesis},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {bachelorthesis}
}

Stoyanova, Y.; Lazarova-Zdravkova, N.; Nemska, V.; Georgieva, N.; Peshev, D.
Application of nanomembrane separation for isolation of natural biologically active components Presentation
European Biotechnology Congress 2021, 23.09.2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@misc{nokey,
title = {Application of nanomembrane separation for isolation of natural biologically active components},
author = {Y. Stoyanova and N. Lazarova-Zdravkova and V. Nemska and N. Georgieva and D. Peshev},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/qpx-kcqe-foc-2021-09-21-at-09_03-GMT-7.mp4},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-09-23},
urldate = {2021-09-23},
abstract = {Recent development of new solvent-stable materials has permitted the application of membrane filtration techniques to different processes in organic solvents and solvent mixtures. The biologically active constituents of plants are traditionally isolated trough solid-liquid extraction and further evaporation of the obtained dilute liquid extracts. Due to their susceptibility to thermal degradation and oxidation, traditional thermal separation technologies result in poor product quality. Significant reduction of the specific energy consumption while preserving product activity during the concentration or fractionation of liquid extracts from rosemary or spent coffee grounds, using nanofiltration, is demonstrated via experimental data and process simulations.
Particular attention is drawn on the current results of a project for fundamental research dealing with application of nanofiltration for valorisation of the waste streams from the essential oil industry. The possibility to fractionate hydrosols and extracts (residual waters) from the steam and hydrodistillation of essential oil plants using nanofiltration was investigated. The separation performance of five commercial nanofiltration membranes with respect to key biologically active components of the studied waste aqueous fractions was predicted based on regression models. Membranes of different MWCO, structure and composition were analysed. The model parameters and the distribution of biologically active compounds in the aqueous effluents and waste plant mass were theoretically predicted using the COSMO-RS method, which has the quantum-chemical basis of the Conductor-like Screening Model (COSMO). The results showed that independently on the membrane material, the polymeric membranes exhibit high retention capability against charged solutes such as the contained in the residual waters phenolic acids. Since the pKa of the phenolic compounds, representatives of the flavonoid family is within the range of pH of the aqueous extracts, their retention or permeation could be controlled by slight variations of the pH. The dissolved in the aqueous fractions essential oil components would be easily permeating through the membranes. These results clearly demonstrated the viability of nanofiltration for isolation of refined polyphenolic fractions from the extracts effluents and for recovery of phenethyl alcohol from hydrosols of Rosa damascena.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)
},
howpublished = {European Biotechnology Congress 2021},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {presentation}
}
Particular attention is drawn on the current results of a project for fundamental research dealing with application of nanofiltration for valorisation of the waste streams from the essential oil industry. The possibility to fractionate hydrosols and extracts (residual waters) from the steam and hydrodistillation of essential oil plants using nanofiltration was investigated. The separation performance of five commercial nanofiltration membranes with respect to key biologically active components of the studied waste aqueous fractions was predicted based on regression models. Membranes of different MWCO, structure and composition were analysed. The model parameters and the distribution of biologically active compounds in the aqueous effluents and waste plant mass were theoretically predicted using the COSMO-RS method, which has the quantum-chemical basis of the Conductor-like Screening Model (COSMO). The results showed that independently on the membrane material, the polymeric membranes exhibit high retention capability against charged solutes such as the contained in the residual waters phenolic acids. Since the pKa of the phenolic compounds, representatives of the flavonoid family is within the range of pH of the aqueous extracts, their retention or permeation could be controlled by slight variations of the pH. The dissolved in the aqueous fractions essential oil components would be easily permeating through the membranes. These results clearly demonstrated the viability of nanofiltration for isolation of refined polyphenolic fractions from the extracts effluents and for recovery of phenethyl alcohol from hydrosols of Rosa damascena.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)

Stoyanova, Y.; Georgieva, N.; Lazarova-Zdravkova, N.; Tsanova, D.; Peshev, D.
BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF CLOVE OIL Conference
XVIII НАУЧНА ПОСТЕРНА СЕСИЯ ЗА МЛАДИ УЧЕНИ, ДОКТОРАНТИ И СТУДЕНТИ НА ХТМУ, UCTM 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF CLOVE OIL},
author = {Y. Stoyanova and N. Georgieva and N. Lazarova-Zdravkova and D. Tsanova and D. Peshev
},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/3FHSI_STOYANOVA_D_Y_Poster_2021.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-06-25},
urldate = {2021-06-25},
booktitle = {XVIII НАУЧНА ПОСТЕРНА СЕСИЯ ЗА МЛАДИ УЧЕНИ, ДОКТОРАНТИ И СТУДЕНТИ НА ХТМУ},
organization = {UCTM},
abstract = {The clove essential oil isolated from the buds of the species Eugenia caryophyllata (Myrtaceae) also found in the literature as Syzygium aromaticum is widely used and widely known for its healing properties. Clove oil has a number of benefits, ranging from anti-inflammatory for oral infections to treating toothache and acne. Due to its widespread use in the pharmaceutical, flavoring and food industries, demand for clove oil is expected to increase to 6000 tonnes by 2022.
The aim of this work is to study the antibacterial and antioxidant activity of clove oil. Gram-negative Escherichia coli K12 407 and Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis 3562 bacterial strains were used to study the inhibitory ability of the clove oil. The agar-diffusion method was used to test the susceptibility of the bacteria when treated with the clove oil. Antioxidant activity was determined spectrophotometrically using the DPPH method.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
The aim of this work is to study the antibacterial and antioxidant activity of clove oil. Gram-negative Escherichia coli K12 407 and Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis 3562 bacterial strains were used to study the inhibitory ability of the clove oil. The agar-diffusion method was used to test the susceptibility of the bacteria when treated with the clove oil. Antioxidant activity was determined spectrophotometrically using the DPPH method.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).

Lazarova-Zdravkova, Nevena; Tsanova, Denitsa; Stoyanova, Yoana; Chilev, Chavdar; Georgieva, Nelly; Peshev, Dimitar
Study of the biological activity of essential oils-water mixtures Journal Article
In: Food Science and Applied Biotechnology, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 48-56, 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Journal Article
@article{Lazarova-Zdravkova2021,
title = {Study of the biological activity of essential oils-water mixtures},
author = {Nevena Lazarova-Zdravkova and Denitsa Tsanova and Yoana Stoyanova and Chavdar Chilev and Nelly Georgieva and Dimitar Peshev},
url = {https://www.ijfsab.com/index.php/fsab/article/view/130/128},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-03-19},
urldate = {2021-03-19},
journal = {Food Science and Applied Biotechnology},
volume = {4},
number = {1},
pages = {48-56},
abstract = {This study aimed to investigate the biological activity of aqueous mixtures of two essential oils. The mixtures were prepared by mixing certain amounts of lavender and clove oils with distilled water at room temperature. In the case of lavender oil, a relatively clear saturated aqueous phase was obtained after mixing with an excess of the essential oil. The clove oil formed stable oil-in-water emulsions. The antibacterial activity of the samples was tested against two model bacterial strains. The growth of the Gram-negative Escherichia coli K12 and the Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis 3562 was determined in 96-well microplates. A more prominent inhibition activity against E. coli K12 strain compared to B. subtilis 3562 for both oil-water mixtures was observed. A disk diffusion test indicated growth inhibition by the lavender oil during the tests against the Gram-positive strain (zones of around 11.7 mm) while clove oil inhibited both bacteria (12 mm - B. subtilis 3562 and 13.66 mm - E. coli K12). The DPPH free radical method showed no antioxidant activity for the aqueous solution of lavender oil. The pure lavender oil exhibited negligible activity compared to the gallic acid reference solution, the clove essential oil, and its emulsion. A quantitative relationship between the content of cloves essential oil in the emulsion and its radical scavenging capacity was demonstrated.},
keywords = {Journal Article},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Georgieva, N.; Lazarova-Zdravkova, N.; Todorova, Y.; Tsanova, D.; Peshev, D.
Antibacterial activity of aqueous solutions of essential oils as an indicator for their content Conference
Poster Abstracts, Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, vol. 35, no. S1, S62-S128 European Biotechnology Congress 2020 Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group., 2021.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {Antibacterial activity of aqueous solutions of essential oils as an indicator for their content},
author = {N. Georgieva and N. Lazarova-Zdravkova and Y. Todorova and D. Tsanova and D. Peshev },
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Praga-Poster_Abstract-p579.pdf
http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/poster-Praga-PDF.pdf},
doi = {10.1080/13102818.2020.1871545},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-02-26},
urldate = {2021-02-26},
booktitle = {Poster Abstracts, Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment},
volume = {35},
number = {S1},
pages = {579},
publisher = {Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.},
organization = {European Biotechnology Congress 2020},
series = {S62-S128},
abstract = {According to market forecasts, annual consumption of essential oils on the world market is growing steadily, reaching 403 thousand tonnes in 2025. The steam distillation of the plant materials to produce essential oils generates vast amounts of aqueous fractions as by-products. Certain amounts of essential oils remain dissolved in these fractions, predetermining their biological activity. If discarded into the environment they have a negative impact on the ecological balance. At the same time, these aqueous fractions are an attractive source of high value-added substances if subjected to valorization. A preliminary appraisal of their quality is required prior to both disposal and valorization. In the present work, antibacterial activity is suggested as an indicator of the content of essential oils in the analyzed products, as far as they are known for their bactericidal potential. To prove the concept, antibacterial activity of pure essential oils dissolved in water in different concentrations was determined using Gram-negative Escherichia coli K12 and Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis 356 bacterial strains. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of essential oils and antibacterial activity using the agardiffusion method were determined.
Funding: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
Funding: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).

Stoyanova, Y.; Georgieva, N.; Lazarova-Zdravkova, N.; Tsanova, D.; Peshev, D.
Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of waste fractions from the essential oil industry Conference Forthcoming
European Biotechnology Congress 2021 Forthcoming.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of waste fractions from the essential oil industry},
author = {Y. Stoyanova and N. Georgieva and N. Lazarova-Zdravkova and D. Tsanova and D. Peshev},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Yoana-Stoyanova-PP-044.pdf},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-00-00},
urldate = {2021-00-00},
organization = {European Biotechnology Congress 2021},
abstract = {Tens of millions of tonnes of waste plant mass are generated every year, which in the areas with traditions in the production of essential oils becomes an environmental problem. Due to the presence of volatile organic components and polyphenolic compounds in the waste products, they are expected to exhibit antimicrobial and antioxidant activity and their uncontrolled disposal has an adverse effect on the ecological balance due to pollution of surface and groundwater. Moreover, valuable substances with biological activity are lost.
The aim of the present work is to study the antibacterial and antioxidant activity of waste materials from the production of essential oils. The accurate determination of the wastes biological activity enables their valorisation. Gram-negative Escherichia coli K12 407 and Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis 3562 bacterial strains were used to study the inhibitory ability of the studied samples. The method of micro-dilution in broth was used to test the susceptibility of the bacteria against the waste fractions. Antioxidant activity was determined spectrophotometrically using the DPPH method.
Keywords: antibacterial, antioxidant, waste product, essential oil.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
The aim of the present work is to study the antibacterial and antioxidant activity of waste materials from the production of essential oils. The accurate determination of the wastes biological activity enables their valorisation. Gram-negative Escherichia coli K12 407 and Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis 3562 bacterial strains were used to study the inhibitory ability of the studied samples. The method of micro-dilution in broth was used to test the susceptibility of the bacteria against the waste fractions. Antioxidant activity was determined spectrophotometrically using the DPPH method.
Keywords: antibacterial, antioxidant, waste product, essential oil.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)
2020

Пешев, Д.
Възможности за оползотворяване на отпадъчните продукти от производството на етерични масла Journal Article
In: Полиграфия, vol. ПроПак, no. 5, pp. 4-7, 2020, ISSN: 0204-9953.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Journal Article
@article{D.Peshev2020b,
title = {Възможности за оползотворяване на отпадъчните продукти от производството на етерични масла},
author = {Д. Пешев},
editor = {Е. Николова},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Peshev_ProPack_Issue_5x2020.pdf},
issn = {0204-9953},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-10-31},
urldate = {2020-10-31},
journal = {Полиграфия},
volume = {ПроПак},
number = {5},
pages = {4-7},
keywords = {Journal Article},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

D.Peshev,
Theoretical assessment of the use of nanofiltration for fractionation of waste aqueous fractions from the essential oil industry Journal Article
In: Bulgarian Chemical Communications, vol. 52,, no. 4, pp. 532-542, 2020.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Journal Article
@article{D.Peshev2020,
title = {Theoretical assessment of the use of nanofiltration for fractionation of waste aqueous fractions from the essential oil industry},
author = {D.Peshev},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/BCC-52-4-2020-532-542-Peshev-MP05-1.pdf},
doi = {10.34049/bcc.52.4.MP05},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-10-19},
urldate = {2020-10-19},
journal = {Bulgarian Chemical Communications},
volume = {52,},
number = {4},
pages = {532-542},
abstract = {The possibility to fractionate hydrosols and extracts (residual waters) from the distillation of representative essential oil plants using nanofiltration was investigated. The rejections of five commercial nanofiltration membranes with respect to key bioactive components were predicted based on regression models. Membranes of different Molecular Weight Cut-Off (MWCO), structure and composition were analyzed. Descriptors in the models were the membrane MWCO and zeta potential, as well as the molecular weight (Mw), octanol-water partition coefficient (log P) and acidity constant (pKa) of the solutes. For consistency, log P and pKa of all studied components were calculated according to the COSMO-RS method, which has the quantum-chemical basis of the Conductor-like Screening Model (COSMO). The distribution of the key components in the two types of effluents under the process conditions was also predicted using COSMO-RS for modelling of the solid-liquid, liquid-liquid and vapor-liquid equilibrium. The calculations were performed using the BIOVIA COSMOsuite software package. The results showed that independently of the membrane material, the polymeric membranes exhibit high retention capability against charged solutes such as the phenolic acids contained in the residual waters. Since the pKa of the phenolic compounds, representatives of the flavonoid family, is within the range of pH of the aqueous extracts, their retention or permeation could be controlled by slight variations of the pH. The essential oil components dissolved in the aqueous fractions are easily permeating through the membranes.},
keywords = {Journal Article},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Цанова, Деница
Биологична активност на етерично масло и хидрозол от лавандула Bachelor Thesis
2020.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Bachelor Thesis
@bachelorthesis{nokey,
title = {Биологична активност на етерично масло и хидрозол от лавандула},
author = {Деница Цанова},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Diplom_work_Denitsa_Tsanova.pdf},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-10-15},
urldate = {2020-10-15},
keywords = {Bachelor Thesis},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {bachelorthesis}
}

Петрова, Кристина
Антибактериална и антиоксидантна активност на масло и розова вода от Роза Дамасцена Masters Thesis
2020.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Masters Thesis
@mastersthesis{nokey,
title = {Антибактериална и антиоксидантна активност на масло и розова вода от Роза Дамасцена},
author = {Кристина Петрова},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/diplomna-rabota-Kristina-25_09_2020_FinalAcknowledgement.pdf},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-10-15},
urldate = {2020-10-15},
keywords = {Masters Thesis},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {mastersthesis}
}

Панайотов, Станислав
Теоретична оценка на използването на нанофилтруването за фракциониране на отпадъчни водни фракции от етерично-маслената промишленост Bachelor Thesis
2020.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: Bachelor Thesis
@bachelorthesis{nokey,
title = {Теоретична оценка на използването на нанофилтруването за фракциониране на отпадъчни водни фракции от етерично-маслената промишленост},
author = {Станислав Панайотов},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/Diplom_work_Panaiotov.pdf},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-10-15},
urldate = {2020-10-15},
keywords = {Bachelor Thesis},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {bachelorthesis}
}

Todorova, Y.; Tsanova, D.; Lazarova-Zdravkova, N.; Chilev, C.; Peshev, D.; Georgieva, N.
XVII НАУЧНА ПОСТЕРНА СЕСИЯ ЗА МЛАДИ УЧЕНИ, ДОКТОРАНТИ И СТУДЕНТИ НА ХТМУ, UCTM 2020.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {IDENTIFICATION OF BIOACTIVE COMPAUNDS IN HYDROSOL AND RESIDUAL WATER AFTER STEAM DESTILATION OF ESSENTIAL OIL CULTURES},
author = {Y. Todorova and D. Tsanova and N. Lazarova-Zdravkova and C. Chilev and D. Peshev and N. Georgieva
},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/3FHSI_TODOROVA_D_Y_Poster_2020.pdf},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-06-26},
urldate = {2020-06-26},
booktitle = {XVII НАУЧНА ПОСТЕРНА СЕСИЯ ЗА МЛАДИ УЧЕНИ, ДОКТОРАНТИ И СТУДЕНТИ НА ХТМУ},
organization = {UCTM},
abstract = {Steam distillation is a common technological process, which guarantees high and sustainable quality of the extracted oils. As a result of the distillation, in addition to the essential oil and the distilled biomass, there are also two another liquid fractions - hydrosol and residual water. Due to the presence of volatile organic components in the hydrosol and polyphenolic compounds in the residual water they are likely to exhibit antimicrobial and antioxidant activity and their uncontrolled disposal could lead to pollution of surface and groundwater and disturb the ecological balance.
The aim of this study is to identify the main components with biological activity in the hydrosol and the residual water of selected four plants – Rosa Damascena, Lavender, Lemon balm and Clove. HPLC and GC chromatographic methods will be used to identify and quantify these components. Determination of antioxidant and antibacterial activity will also be performed.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
The aim of this study is to identify the main components with biological activity in the hydrosol and the residual water of selected four plants – Rosa Damascena, Lavender, Lemon balm and Clove. HPLC and GC chromatographic methods will be used to identify and quantify these components. Determination of antioxidant and antibacterial activity will also be performed.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14).
Tsanova, D.; Lazarova-Zdravkova, N.; Peshev, D.; Georgieva, N.; Chilev, Ch.; Todorova, Y.; Yonkova, V.
XVII НАУЧНА ПОСТЕРНА СЕСИЯ ЗА МЛАДИ УЧЕНИ, ДОКТОРАНТИ И СТУДЕНТИ НА ХТМУ, UCTM 2020.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conference
@conference{nokey,
title = {APPLICATION OF NANOMEMBRANE SEPARATION FOR UTILIZATION OF WASTE PRODUCTS FROM THE ESSENTIAL OIL PRODUCTION},
author = {D. Tsanova and N. Lazarova-Zdravkova and D. Peshev and N. Georgieva and Ch. Chilev and Y. Todorova and V. Yonkova},
url = {http://www.nanoessential.eu/wp-content/uploads/3FHSI_TSANOVA_G_D.pdf},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-06-26},
urldate = {2020-06-26},
booktitle = {XVII НАУЧНА ПОСТЕРНА СЕСИЯ ЗА МЛАДИ УЧЕНИ, ДОКТОРАНТИ И СТУДЕНТИ НА ХТМУ},
organization = {UCTM},
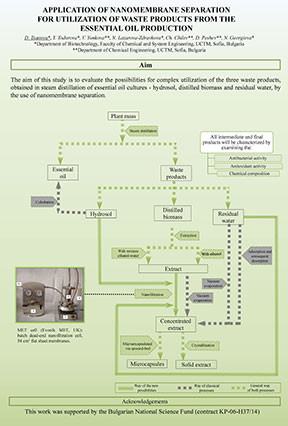
abstract = {Steam distillation is a widely used process for essential oil extraction. Besides the final product a vast amount of other fractions are obtained – hydrosol, distilled biomass and residual water. Depending on the characteristics of the oil-bearing plants a secondary distillation – cohobation could be carried out in order to recover additional amount of the essential oil. Very often cohobation is unfeasible and as a result hydrosols are disposed in the environmental. Residual water fraction represents hot water extracts from the plant material.. They are rich of components with antibacterial and antioxidant activity. In the practice they are often neglected and disposed in the environment. Usually distilled biomass is treated as a waste. However it contains various biologically active components that could be extractable with organic solvents such as ethanol.
In this work nanofiltration is regarded as a useful technology for valorization of these waste fractions.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)},
keywords = {Conference},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
In this work nanofiltration is regarded as a useful technology for valorization of these waste fractions.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Bulgarian National Science Fund (contract KP-06-H37/14)